6.7 The Color View
The Color View is accessible from the top toolbar by pressing on the color palette button from within any screen and provides multiple ways to select and manipulate colors. It consists of the following tabs:
- CIE
Displays a CIE 1931 horseshoe-shaped color picker (xy). - HUE
Displays a Hue and Saturation-based color picker. - CCT
Provides a picker specifically designed for Correlated Color Temperature (CCT) and Tint (Magenta/Green Shift). - FadersDisplays separate faders for adjusting colors in HSI, RGB, and CMY modes.
- Gels
Provides a library of color gels from various manufacturers. - Moods
Offers a selection of predefined colors based on different light sources and moods.
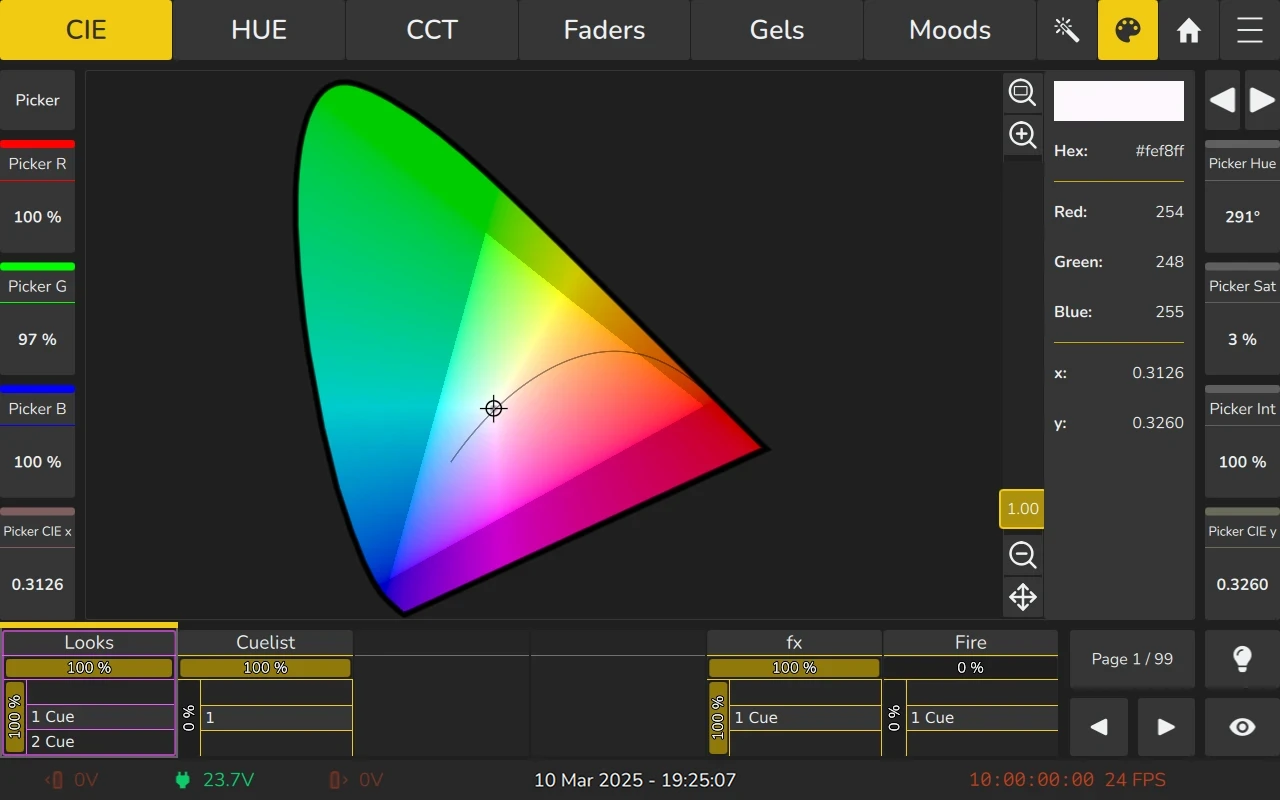
The Color View offers maximum flexibility when working with modern multi-emitter LED fixtures. When selecting colors in any of the views, EDGE calculates the output based on the fixture’s emitter data, supporting up to nine different LED emitters. The calibration is calculated based on a D65 whitepoint.
The individual output color for each fixture is determined based on its color mixing data, which can be adjusted in the Library Editor.
If the targeted color falls outside a fixture’s achievable color space, EDGE automatically maps it to the closest possible color within that fixture’s range.
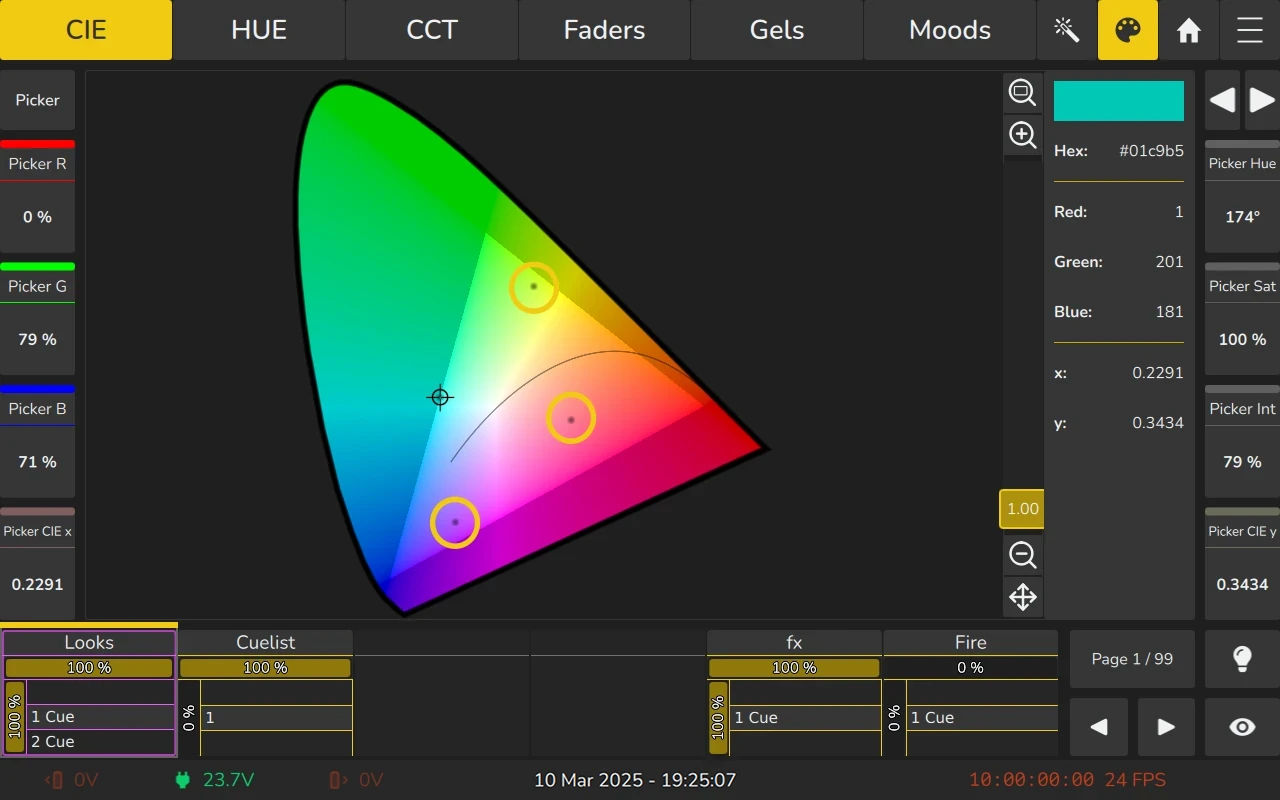
When multiple fixture types with different color spaces are selected, this can be observed in the Color Picker, where the light source dots may separate at certain boundaries, visually representing the differences in their color capabilities.
Using the color wheels with Color Views
Fixtures without color mixing can also be controlled using the Color Views. For these fixtures, the available colors are determined by the filters on their color wheel, and the corresponding color space is displayed in the Color Picker.
Since a color wheel offers only a limited number of discrete colors, only a small subset of selectable points is available in the picker, each representing an individual filter position.
These color wheel spaces are typically much smaller than those of RGB or multi-emitter fixtures and may be visually overshadowed in the Color Picker when mixed with fixtures that support full color mixing.
Editing Emitter Data in the Library Editor
Some fixtures already include emitter data in the library. For fixtures without predefined emitter data, users can manually enter custom light source data by using the Color Mixing button in the Library Editor.
This feature allows for self-calibration of fixtures on a per-type basis. If there are differences between individual fixtures of the same type, users can create copies of the definition and patch them accordingly to reflect variations in emitter data distribution.
This results in a highly optimized and precise color selection across multiple color channels, accommodating different emitter intensities and color mixing systems, including HSI and CMY.
Older or retro-style fixtures that rely on color wheels instead of LED mixing are also fully supported. For the best results, fixtures should be used in RAW mode, where internal fixture-based color adjustments are disabled, ensuring that the selected color spectrum is applied as intended.
Targeted Output Color
The selected color as manipulated through the color picker, encoders, or faders. This represents the intended color and is displayed in the right section of the color picker.
6.7.1 Changing color values using the Encoders.
Whenever a color view is open, the encoders can be used to adjust Red / Green / Blue, Hue / Saturation / Intensity and x as well as y. Colors adjusted here will always use the calibration algorithms and make best use of all emitters in the fixture.
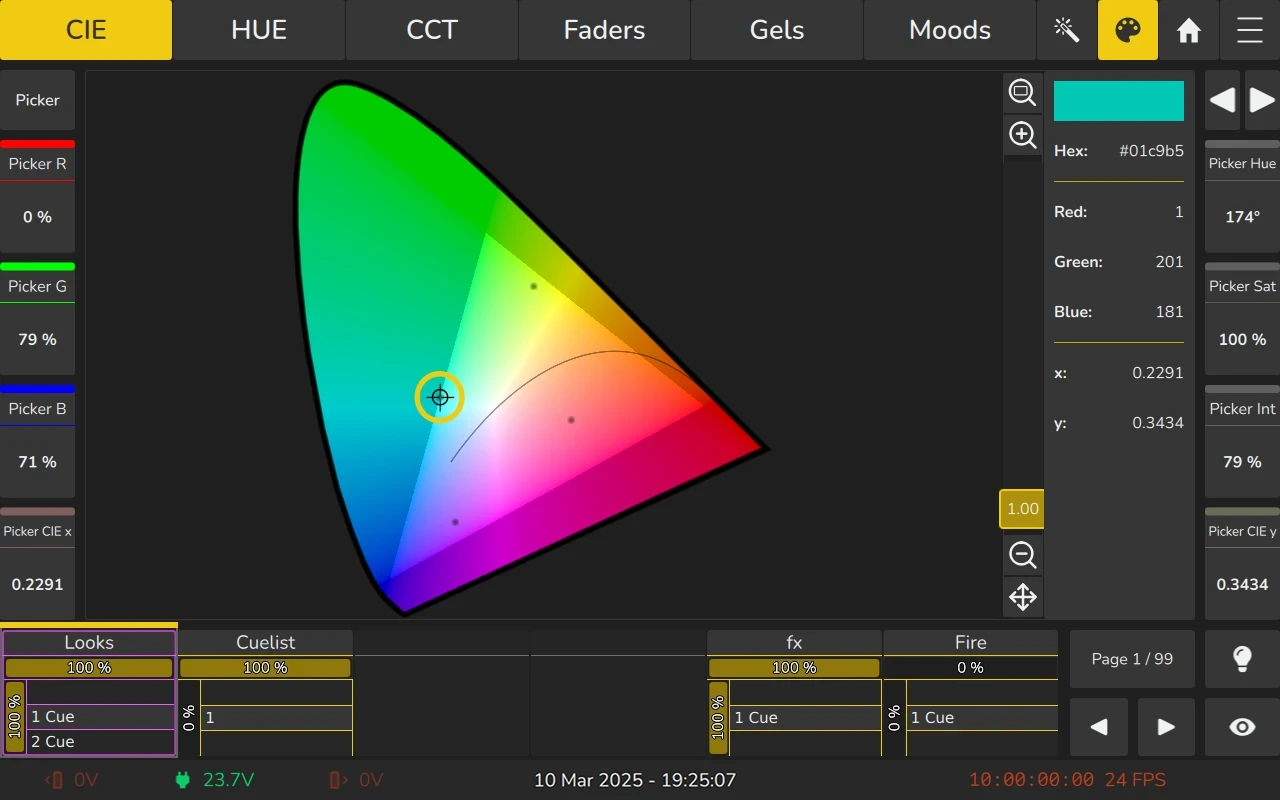
Individual Output Color
The Individual Output Color represents the actual color output of each selected fixture. It is visually indicated by dots in the Color Picker.
Due to variations in emitter configurations and fixture-specific color mixing capabilities, the channel output for each fixture may differ from the targeted color. This ensures that the desired color appearance is maintained as closely as possible across different light sources.
If a color mixing effect (such as a rainbow fade wave) is applied, each fixture's output color will be adjusted accordingly, as shown in the figure below.
6.7.2 CIE 1931 Color Picker
The CIE Color Picker displays a horseshoe representation of the color space. By default the color space of the last selected fixture is shown. You can further customize the displayed color spaces in the Magic Wand Menu.
To select a color, simply click and drag the target on the color picker.
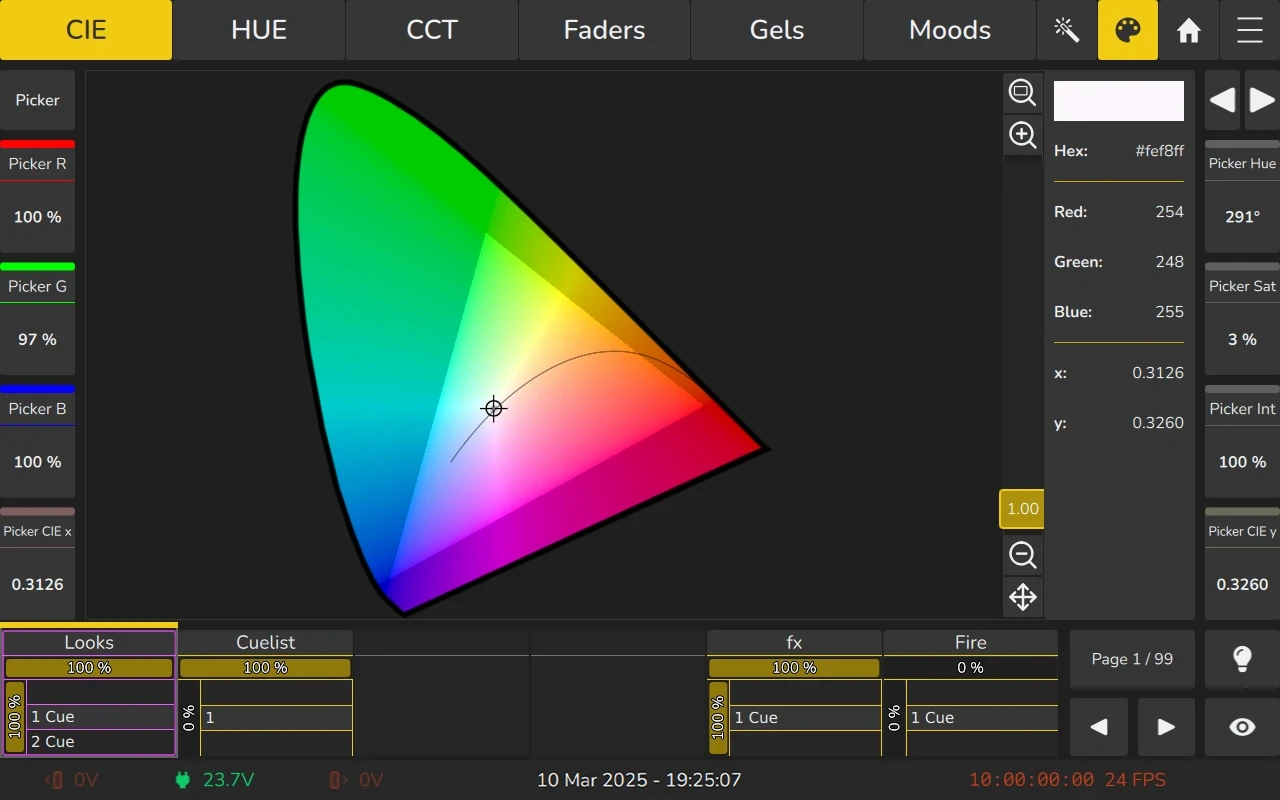
6.7.3 HUE (Hue and Saturation) Color Picker
The HUE Color Picker displays a circular color picker with the fully saturated colors on the outside, and less saturated colors in the center.
To select a color, simply click and drag the target on the color picker.
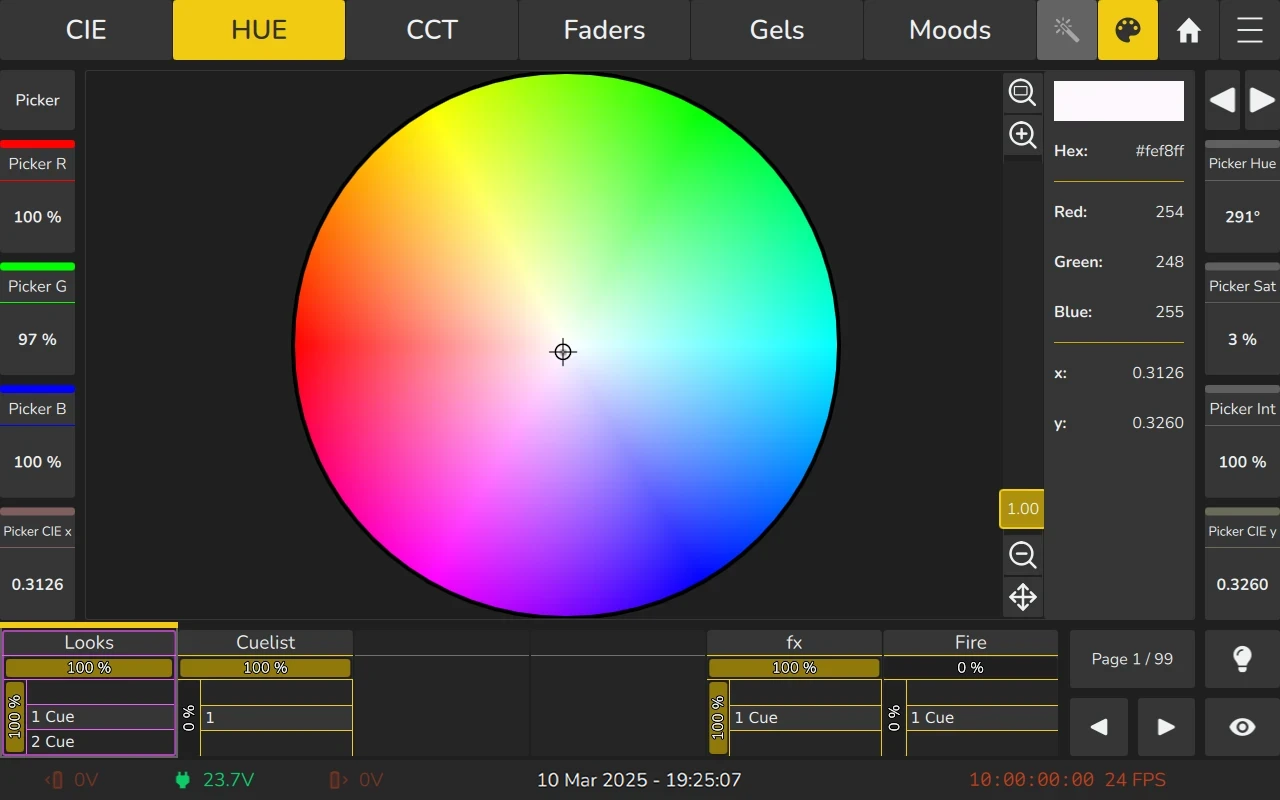
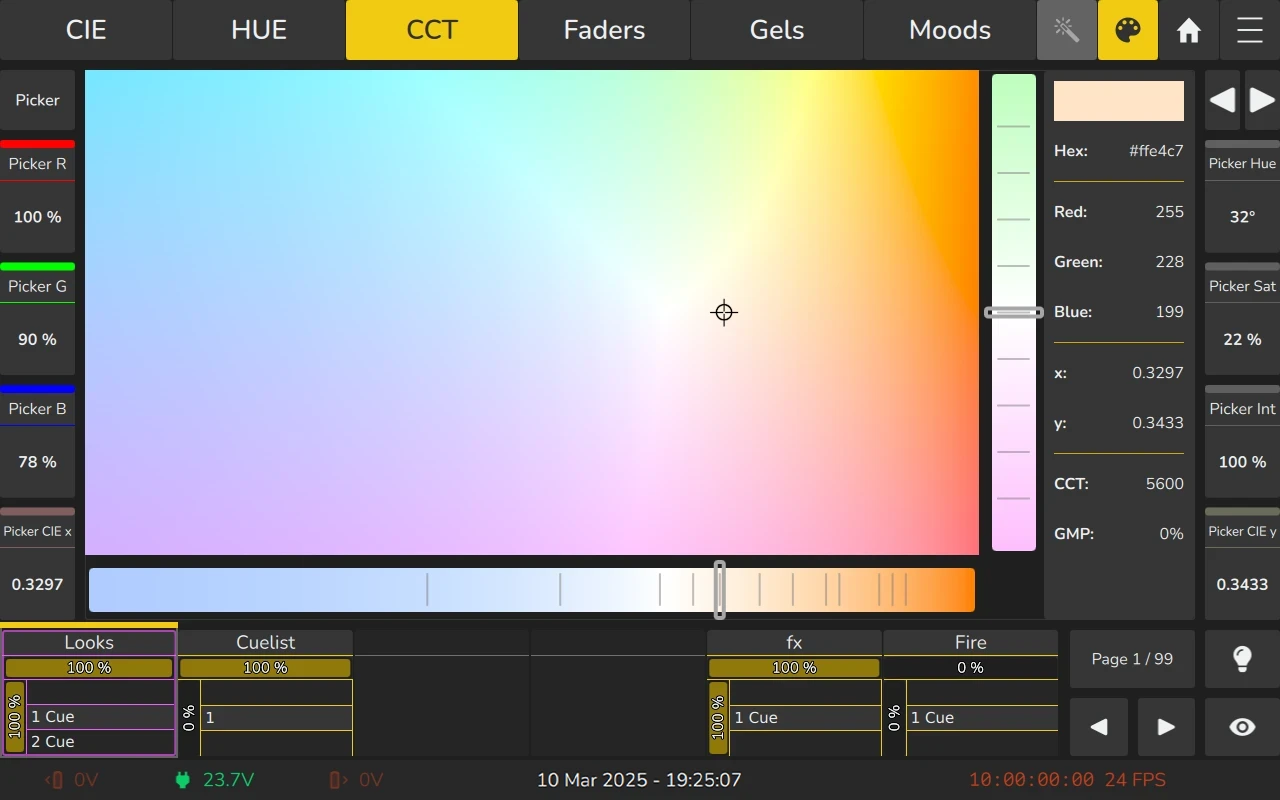
6.7.4 CCT (Correlated color temperature and Tint) Picker
The CCT / Tint color picker offers a great way to select a certain color temperature and green / magenta point, also known as tint.
Warm colors are on the right side, whereas the left side gets colder. The slider on the bottom adjusts the color temperature and offers various snap-points at common color temperatures.
The vertical direction controls the green / magenta shift, with green being in the top area, neutral in the center and magenta shift in the bottom. The slider on the right side can be used to adjust the green / magenta shift and offers snap points at certain intervals.
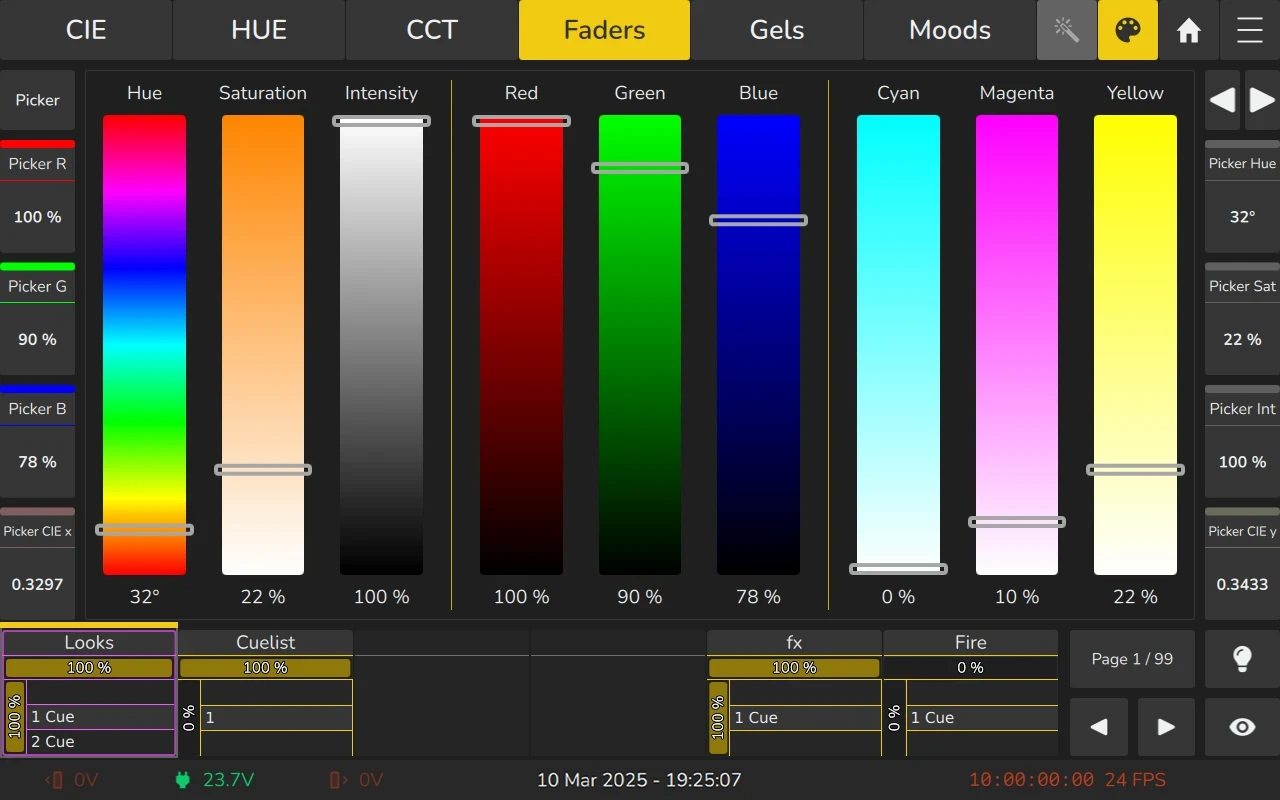
6.7.5 Color Faders
The Color Faders view displays multiple faders which can be used to adjust the target color of the color algorithms. The sliders auto-update depending on the other sliders being dragged.
6.7.6 Gels
The Gels Pool displays a number of predefined color filters /gels, both for 6500K White Point and 3200K White Point.
If you have search bars for pools enabled in the Settings (Learn more :Enable Search in Pool Views), you can also filter and search the gels.
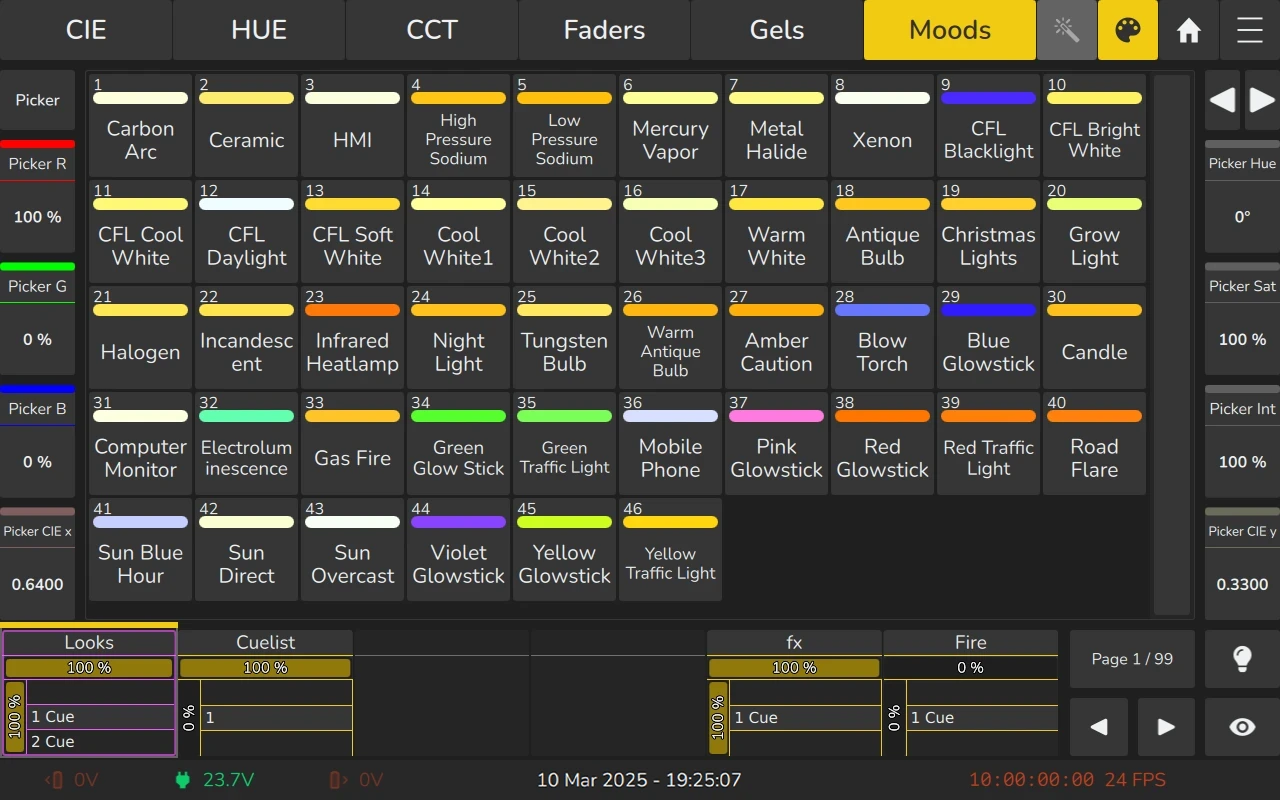
6.7.7 Moods / Source Replication
The Moods Pool displays a number of moods and allows predefined light sources to be selected for replication.